Acidic Patch Mutant H2AE92K Recombinant Nucleosome with Linker DNA, Biotinylated
{"url":"https://www.epicypher.com/products/nucleosomes/mutant-nucleosomes/acidic-patch-mutant-h2ae92k-recombinant-nucleosome-with-linker-dna-biotinylated","add_this":[{"service":"facebook","annotation":""},{"service":"email","annotation":""},{"service":"print","annotation":""},{"service":"twitter","annotation":""},{"service":"linkedin","annotation":""}],"gtin":null,"id":705,"bulk_discount_rates":[],"can_purchase":true,"meta_description":"Acidic patch mutant recombinant mononucleosomes (biotinylated H2AE92K with linker DNA), functionally validated with exceptional quality controls. Useful for chromatin binding, enzymatic, and structural studies.","category":["Nucleosomes","Nucleosomes/Mutant Nucleosomes","Nucleosomes/Mutant Nucleosomes/Acidic Patch Nucleosomes"],"AddThisServiceButtonMeta":"","main_image":{"data":"https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-y9o92/images/stencil/{:size}/products/705/1227/2021.05.05_acidic_patch_nuc_RGB_white_border_LS_icon_thumbnail_board_2__41959__47696.1717694541.png?c=2","alt":"Acidic Patch Mutant H2AE92K Recombinant Nucleosome with Linker DNA, Biotinylated"},"add_to_wishlist_url":"/wishlist.php?action=add&product_id=705","shipping":{"calculated":true},"num_reviews":0,"weight":"0.01 LBS","custom_fields":[{"id":"492","name":"Pack size","value":"50 µg"}],"sku":"16-2030","description":"<div class=\"product-general-info\">\n <ul class=\"product-general-info__list-left\">\n <li class=\"product-general-info__list-item\">\n <strong>Species: </strong>Human\n </li>\n <li class=\"product-general-info__list-item\">\n <strong>Source: </strong><em>E. coli</em> & synthetic DNA\n </li>\n </ul>\n <ul class=\"product-general-info__list-right\">\n <li class=\"product-general-info__list-item\">\n <strong>Tag: </strong>Biotinylated\n </li>\n <li class=\"product-general-info__list-item\">\n <strong>Molecular Weight: </strong>231,880 Da\n </li>\n </ul>\n</div>\n<div class=\"service_accordion product-droppdown\">\n <div class=\"container\">\n <div id=\"prodAccordion\">\n <div id=\"ProductDescription\" class=\"Block Panel current\">\n <h3 class=\"sub-title1\">Description</h3>\n <div class=\"ProductDescriptionContainer product-droppdown__section-description-specific\">\n <p>\n The acidic patch is a negatively charged region of the nucleosome surface that serves as a conserved\n interaction hub for neighboring nucleosomes and chromatin binding proteins, often via salt bridges with\n arginine anchors [1]. The acidic patch plays a critical role in chromatin condensation and chromatin\n remodeling [1-3]. Recombinant mononucleosomes containing acidic patch mutations can be used to study the\n biological functions of the acidic patch.\n </p>\n <p>\n H2AE92K Recombinant Nucleosome with Linker DNA consists of 199 base pairs of DNA wrapped around an octamer\n core of\n histone proteins (two each of H2A, H2B, H3.1, and H4) to form a nucleosome, the basic repeating unit of\n chromatin. The\n 5’ biotin-TEG DNA consists of a core 147 bp 601 nucleosome assembly sequence [4] flanked by 26 bp linker\n sequences as\n underlined below. Histone H2A contains a glutamate-to-lysine (E-to-K) substitution at position 92 (H2AE92K).\n H2AE92\n resides in the H2A C-terminal extension and mediates chromatin binding with factors such as H4-N-terminal\n tail, LANA,\n RCC1, IL-33, Sir3, HMGN2, and SMARCA5/SNF2h, an ATPase subunit of the ISWI family of chromatin remodeling\n complexes\n [1-3]. H2AE92K disrupts binding with SMARCB1/BAF47, a subunit of the SWI/SNF (BAF) family of chromatin\n remodeling\n complexes. These complexes serve a critical role in cell division, cell and tissue differentiation, and\n development, and\n SWI/SNF complex malfunction has been linked to over 20% of human cancers [5].\n </p>\n </div>\n </div>\n </div>\n <div id=\"prodAccordion\">\n <div id=\"ProductDescription\" class=\"Block Panel current\">\n <h3 class=\"sub-title1\">Validation Data</h3>\n <div class=\"ProductDescriptionContainer product-droppdown__section-description-specific\">\n <section class=\"image-picker\">\n <div class=\"image-picker__left\">\n <div class=\"image-picker__main-content_active image-picker__main-content\">\n <div class=\"image-picker__header-content\">\n <button class=\"image-picker__left-arrow\">\n <svg class=\"image-picker__svg-left\" width=\"24\" height=\"24\" viewBox=\"0 0 24 24\">\n <path d=\"M16.67 0l2.83 2.829-9.339 9.175 9.339 9.167-2.83 2.829-12.17-11.996z\" />\n </svg>\n </button>\n <a href=\"/content/images/products/nucleosomes/16-2030-protein-gel-data.jpeg\" target=\"_blank\"\n class=\"image-picker__main-image-link\"><img alt=\"16-2030-protein-gel-data\"\n src=\"/content/images/products/nucleosomes/16-2030-protein-gel-data.jpeg\"\n class=\"image-picker__main-image\" />\n <span class=\"image-picker__main-image-caption\">(Click to enlarge)</span></a>\n <button class=\"image-picker__right-arrow\">\n <svg class=\"image-picker__svg-right\" width=\"24\" height=\"24\" viewBox=\"0 0 24 24\">\n <path d=\"M7.33 24l-2.83-2.829 9.339-9.175-9.339-9.167 2.83-2.829 12.17 11.996z\" />\n </svg>\n </button>\n </div>\n <p>\n <span class=\"image-picker__span-content\"><strong>Figure 1: Protein gel gata </strong><br />\n Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE gel of proteins in H2AE92K recombinant nucleosome (1 µg) demonstrates the\n purity of histones in the preparation. Sizes of molecular weight markers and positions of the core\n histones (H2AE92K, H2B, H3 and H4) are indicated.\n </span>\n </p>\n </div>\n <div class=\"image-picker__main-content\">\n <div class=\"image-picker__header-content\">\n <button class=\"image-picker__left-arrow\">\n <svg class=\"image-picker__svg-left\" width=\"24\" height=\"24\" viewBox=\"0 0 24 24\">\n <path d=\"M16.67 0l2.83 2.829-9.339 9.175 9.339 9.167-2.83 2.829-12.17-11.996z\" />\n </svg>\n </button>\n <a href=\"/content/images/products/nucleosomes/16-2030-dna-gel-data.jpeg\" target=\"_blank\"\n class=\"image-picker__main-image-link\"><img alt=\"16-2030-dna-gel-data\"\n src=\"/content/images/products/nucleosomes/16-2030-dna-gel-data.jpeg\"\n class=\"image-picker__main-image\" />\n <span class=\"image-picker__main-image-caption\">(Click to enlarge)</span></a>\n <button class=\"image-picker__right-arrow\">\n <svg class=\"image-picker__svg-right\" width=\"24\" height=\"24\" viewBox=\"0 0 24 24\">\n <path d=\"M7.33 24l-2.83-2.829 9.339-9.175-9.339-9.167 2.83-2.829 12.17 11.996z\" />\n </svg>\n </button>\n </div>\n <p>\n <span class=\"image-picker__span-content\"><strong>Figure 2: DNA gel data </strong><br />\n\n H2AE92K recombinant nucleosome resolved by native PAGE and stained with ethidium bromide to\n visualize DNA. <strong>Lane 1</strong>: Free DNA (EpiCypher <a\n href=\"/products/nucleosomes/nucleosome-assembly-601-sequence-dna-199-bp-biotinylated\"\n target=\"_blank\">18-2044</a>; 100 ng). Biotinylated DNA can dimerize (band at ~400 bp). <strong>Lane 2</strong>:\n Intact H2AE92K recombinant nucleosomes (400 ng).\n </span>\n </p>\n </div>\n <div class=\"image-picker__main-content\">\n <div class=\"image-picker__header-content\">\n <button class=\"image-picker__left-arrow\">\n <svg class=\"image-picker__svg-left\" width=\"24\" height=\"24\" viewBox=\"0 0 24 24\">\n <path d=\"M16.67 0l2.83 2.829-9.339 9.175 9.339 9.167-2.83 2.829-12.17-11.996z\" />\n </svg>\n </button>\n <a href=\"/content/images/products/nucleosomes/16-2030-functional-binding-assay.jpeg\" target=\"_blank\"\n class=\"image-picker__main-image-link\">\n <img alt=\"16-2030-functional-binding-assay\"\n src=\"/content/images/products/nucleosomes/16-2030-functional-binding-assay.jpeg\"\n class=\"image-picker__main-image\" />\n <span class=\"image-picker__main-image-caption\">(Click to enlarge)</span>\n </a>\n <button class=\"image-picker__right-arrow\">\n <svg class=\"image-picker__svg-right\" width=\"24\" height=\"24\" viewBox=\"0 0 24 24\">\n <path d=\"M7.33 24l-2.83-2.829 9.339-9.175-9.339-9.167 2.83-2.829 12.17 11.996z\" />\n </svg>\n </button>\n </div>\n <p>\n <span class=\"image-picker__span-content\">\n <strong>Figure 3: Functional binding assay </strong><br />\n The presence of the acidic patch mutations disrupts LANA peptide binding to recombinant nucleosomes\n (WT control, EpiCypher <a\n href=\"/products/nucleosomes/mononucleosomes-recombinant-199x601-dna-biotinylated\"\n target=\"_blank\">16-2044</a>; H2AE61A, EpiCypher <a\n href=\"/products/nucleosomes/mutant-nucleosomes/acidic-patch-mutant-h2ae61a-recombinant-nucleosome-with-linker-dna-biotinylated\"\n target=\"_blank\">16-2029</a>; H2AE92K, EpiCypher 16-2030;\n H2BE105A,E113A, EpiCypher <a\n href=\"/products/nucleosomes/mutant-nucleosomes/acidic-patch-mutant-h2be105a-e113a-recombinant-nucleosome-with-linker-dna-biotinylated\"\n target=\"_blank\">16-2031</a>). The binding of GST-tagged LANA peptide to biotinylated\n recombinant nucleosomes was assessed by AlphaLISA assay using Streptavidin Donor Beads and\n Glutathione Acceptor Beads (PerkinElmer). The presence of H2A acidic patch mutations completely\n blocks LANA binding, while H2B mutations cause a decrease in LANA binding affinity.\n </span>\n </p>\n </div>\n </div>\n <aside class=\"image-picker__right\">\n <div class=\"image-picker__gallery\">\n <img alt=\"16-2030-protein-gel-data-test\"\n src=\"/content/images/products/nucleosomes/16-2030-protein-gel-data.jpeg\" width=\"200\"\n class=\"image-picker__side-image image-picker__side-image_active\" role=\"button\" />\n <img alt=\"16-2030-dna-gel-data-test\"\n src=\"/content/images/products/nucleosomes/16-2030-dna-gel-data.jpeg\" class=\"image-picker__side-image\"\n role=\"button\" />\n <img alt=\"16-2030-functional-binding-assay-test\"\n src=\"/content/images/products/nucleosomes/16-2030-functional-binding-assay.jpeg\"\n class=\"image-picker__side-image\" role=\"button\" />\n </div>\n </aside>\n </section>\n </div>\n </div>\n </div>\n <div id=\"prodAccordion\">\n <div id=\"ProductDescription\" class=\"Block Panel\">\n <h3 class=\"sub-title1\">Technical Information</h3>\n <div class=\"ProductDescriptionContainer product-droppdown__section-description\">\n <div class=\"product-tech-info\">\n <div class=\"product-tech-info__line-item\">\n <div class=\"product-tech-info__line-item-left\">\n <b>Storage</b>\n </div>\n <div class=\"product-tech-info__line-item-right\">\n Stable for six months at -80°C from date of receipt. For best results, aliquot and avoid freeze/thaws.\n </div>\n </div>\n <div class=\"product-tech-info__line-item\">\n <div class=\"product-tech-info__line-item-left\">\n <b>Formulation</b>\n </div>\n <div class=\"product-tech-info__line-item-right\">\n 10 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.5, 25 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, 2 mM DTT, 20% glycerol (27.3 μg protein, 50 μg DNA + protein).\n </div>\n </div>\n </div>\n </div>\n </div>\n </div>\n <div id=\"prodAccordion\">\n <div id=\"ProductDescription\" class=\"Block Panel\">\n <h3 class=\"sub-title1\">Application Notes</h3>\n <div class=\"ProductDescriptionContainer product-droppdown__section-description\">\n <p>\n H2AE92K mononucleosome is highly purified and suitable for a variety of applications to test the effect of\n acidic patch mutation on enzymatic activity or chromatin binding. The biotinylated DNA enables affinity\n binding applications. For a corresponding unmodified control, we recommend EpiCypher <a\n href=\"/products/nucleosomes/mononucleosomes-recombinant-199x601-dna-biotinylated\"\n target=\"_blank\">16-2044</a>.\n </p>\n </div>\n </div>\n </div>\n <div id=\"prodAccordion\">\n <div id=\"ProductDescription\" class=\"Block Panel\">\n <h3 class=\"sub-title1\">DNA Sequence</h3>\n <div class=\"ProductDescriptionContainer product-droppdown__section-description\">\n <p style=\"line-break: anywhere\">\n 5’Bio-TEG<br>\n <u>GGACCCTATACGCGGCCGCCGAATTCC</u>TGGAGAATCCCGGTCTGCAGGCCGCTCAATTGGTCGTAGACAGCTCTAGCACCGCTTAAACGCACGTACGCGCTGTCCCCCGCGTTTTAACCGCCAAGGGGATTACTCCCTAGTCTCCAGGCACGTGTCAGATATATACATCCTGT<u>GGATCCGCCGGTCGCGAACAGCGACC</u>3’\n </p>\n </div>\n </div>\n </div>\n <div id=\"prodAccordion\">\n <div id=\"ProductDescription\" class=\"Block Panel\">\n <h3 class=\"sub-title1\">Gene & Protein Information</h3>\n <div class=\"ProductDescriptionContainer product-droppdown__section-description\">\n <div class=\"product-tech-info\">\n <div class=\"product-tech-info__line-item\">\n <div class=\"product-tech-info__line-item-left\">\n <b>UniProt ID</b>\n </div>\n <div class=\"product-tech-info__line-item-right\">\n H2A - P04908 (alt. names: H2A type 1-B/E, H2A.2, H2A/a,\n H2A/m)<br />\n H2B - O60814 (alt. names: H2B K, HIRA-interacting protein 1)<br />\n H3.1 - P68431 (alt. names: H3, H3/a, H3/b, H3/c, H3/d)<br />\n H4 - P62805\n </div>\n </div>\n </div>\n </div>\n </div>\n </div>\n <div id=\"prodAccordion\">\n <div id=\"ProductDescription\" class=\"Block Panel\">\n <h3 class=\"sub-title1\">References</h3>\n <div class=\"ProductDescriptionContainer product-droppdown__section-description\">\n <strong>Background References:</strong>\n <br />\n [1] Kalashnikova et al. <em>J. R. Soc. Interface</em> (2013). PMID:\n <a href=\"https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23446052/\" target=\"_blank\"\n title=\"The role of the nucleosome acidic patch in modulating higher order chromatin structure\">23446052</a><br />\n [2] Levendosky & Bowman <em>eLife</em> (2019). PMID:\n <a href=\"https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31094676/\" target=\"_blank\"\n title=\"Asymmetry between the two acidic patches dictates the direction of nucleosome sliding by the ISWI chromatin remodeler\">31094676</a><br />\n [3] Gamarra et al. <em>eLife</em> (2018). PMID:\n <a href=\"https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29664398/\" target=\"_blank\"\n title=\"The nucleosomal acidic patch relieves auto-inhibition by the ISWI remodeler SNF2h\">29664398</a><br />\n [4] Lowary & Widom <em>J. Mol. Biol.</em> (1998). PMID:\n <a href=\"https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9514715/\" target=\"_blank\"\n title=\"New DNA sequence rules for high affinity binding to histone octamer and sequence-directed nucleosome positioning\">9514715</a><br />\n [5] Valencia et al. <em>Cell</em> (2019). PMID:\n <a href=\"https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31759698/\" target=\"_blank\"\n title=\"Recurrent SMARCB1 Mutations Reveal a Nucleosome Acidic Patch Interaction Site That Potentiates mSWI/SNF Complex Chromatin Remodeling\">31759698</a><br />\n </div>\n </div>\n </div>\n <div id=\"prodAccordion\">\n <div id=\"ProductDescription\" class=\"Block Panel\">\n <h3 class=\"sub-title1\">Documents & Resources</h3>\n <div class=\"ProductDescriptionContainer product-droppdown__section-description\">\n <div class=\"product-documents\">\n <a href=\"/content/documents/tds/16-2030.pdf\" target=\"_blank\" class=\"product-documents__link\">\n <svg version=\"1.1\" id=\"Layer_1\" xmlns=\"http://www.w3.org/2000/svg\"\n xmlns:xlink=\"http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink\" x=\"0px\" y=\"0px\" viewBox=\"0 0 228 240\"\n style=\"enable-background: new 0 0 228 240\" xml:space=\"preserve\" class=\"product-documents__icon\"\n alt=\"16-2030 Datasheet\">\n <g>\n <path class=\"product-documents__svg-pdf\" d=\"M191.92,68.77l-47.69-47.69c-1.33-1.33-3.12-2.08-5.01-2.08H45.09C41.17,19,38,22.17,38,26.09v184.36\n c0,3.92,3.17,7.09,7.09,7.09h141.82c3.92,0,7.09-3.17,7.09-7.09V73.8C194,71.92,193.25,70.1,191.92,68.77z M177.65,77.06h-41.7\n v-41.7L177.65,77.06z M178.05,201.59H53.95V34.95h66.92v47.86c0,5.14,4.17,9.31,9.31,9.31h47.86V201.59z\" />\n </g>\n <rect x=\"20\" y=\"112\" class=\"product-documents__svg-background\" width=\"146\" height=\"76\" />\n <g>\n <path class=\"product-documents__svg-pdf\" d=\"M23.83,125.68h22.36c5.29,0,9.41,1.33,12.35,4c2.94,2.67,4.42,6.39,4.42,11.18c0,4.78-1.47,8.51-4.42,11.18\n c-2.94,2.67-7.06,4-12.35,4H34.59v18.29H23.83V125.68z M44.81,147.9c5.38,0,8.07-2.32,8.07-6.97c0-2.39-0.67-4.16-2-5.31\n c-1.33-1.15-3.36-1.73-6.07-1.73H34.59v14.01H44.81z\" />\n <path class=\"product-documents__svg-pdf\" d=\"M69.92,125.68h18.91c5.29,0,9.84,0.97,13.66,2.9c3.82,1.93,6.74,4.72,8.76,8.35\n c2.02,3.63,3.04,7.98,3.04,13.04c0,5.06-1,9.42-3,13.08c-2,3.66-4.91,6.45-8.73,8.38c-3.82,1.93-8.4,2.9-13.73,2.9H69.92V125.68z\n M88.07,165.63c10.35,0,15.52-5.22,15.52-15.66c0-10.4-5.17-15.59-15.52-15.59h-7.38v31.26H88.07z\" />\n <path class=\"product-documents__svg-pdf\"\n d=\"M122.57,125.68h32.84v8.49h-22.22v11.18h20.84v8.49h-20.84v20.49h-10.63V125.68z\" />\n </g>\n </svg>\n <span class=\"product-documents__info\">Technical Datasheet</span>\n </a>\n </div>\n </div>\n </div>\n </div>\n </div>\n</div>","tags":[],"warranty":"","price":{"without_tax":{"formatted":"$475.00","value":475,"currency":"USD"},"tax_label":"Sales Tax"},"detail_messages":"","availability":"","page_title":"Acidic Patch Mutant Recombinant Nucleosome | H2AE92K with Linker DNA, Biotinylated","cart_url":"https://www.epicypher.com/cart.php","max_purchase_quantity":0,"mpn":null,"upc":null,"options":[],"related_products":[{"id":1148,"sku":"16-2029","name":"Acidic Patch Mutant H2AE61A Recombinant Nucleosome with Linker DNA, Biotinylated","url":"https://www.epicypher.com/products/nucleosomes/mutant-nucleosomes/acidic-patch-mutant-h2ae61a-recombinant-nucleosome-with-linker-dna-biotinylated","availability":"","rating":null,"brand":{"name":null},"category":["Nucleosomes","Nucleosomes/Mutant Nucleosomes","Nucleosomes/Mutant Nucleosomes/Acidic Patch Nucleosomes"],"summary":"\n \n \n Species: Human\n \n \n Source: E. coli & synthetic DNA\n \n \n \n ","image":{"data":"https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-y9o92/images/stencil/{:size}/products/1148/1221/2021.05.05_acidic_patch_nuc_RGB_white_border_LS_icon_thumbnail_board_2__41959.1717092961.png?c=2","alt":"Acidic Patch Mutant H2AE61A Recombinant Nucleosome with Linker DNA, Biotinylated"},"images":[{"data":"https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-y9o92/images/stencil/{:size}/products/1148/1221/2021.05.05_acidic_patch_nuc_RGB_white_border_LS_icon_thumbnail_board_2__41959.1717092961.png?c=2","alt":"Acidic Patch Mutant H2AE61A Recombinant Nucleosome with Linker DNA, Biotinylated"}],"date_added":"30th May 2024","pre_order":false,"show_cart_action":true,"has_options":false,"stock_level":null,"low_stock_level":null,"qty_in_cart":0,"custom_fields":[{"id":1315,"name":"Pack Size","value":"50 µg"}],"num_reviews":null,"weight":{"formatted":"0.00 LBS","value":0},"demo":false,"add_to_cart_url":"https://www.epicypher.com/cart.php?action=add&product_id=1148","price":{"without_tax":{"currency":"USD","formatted":"$475.00","value":475},"tax_label":"Sales Tax"},"add_to_wishlist_url":"/wishlist.php?action=add&product_id=1148"},{"id":792,"sku":"16-2044","name":"Mononucleosomes, Recombinant, 199x601 DNA, Biotinylated","url":"https://www.epicypher.com/products/nucleosomes/mononucleosomes-recombinant-199x601-dna-biotinylated","availability":"","rating":null,"brand":{"name":null},"category":["Nucleosomes","Nucleosomes/Methyl DNA Designer Nucleosomes"],"summary":"\n \n \n Species: Human\n \n \n Source: E. coli & synthetic DNA\n \n \n \n ","image":{"data":"https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-y9o92/images/stencil/{:size}/products/792/931/mononucleosomes-recombinant-199x601-dna-biotinylated__61382.1645734522.jpg?c=2","alt":"Mononucleosomes, Recombinant, 199x601 DNA, Biotinylated"},"images":[{"data":"https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-y9o92/images/stencil/{:size}/products/792/931/mononucleosomes-recombinant-199x601-dna-biotinylated__61382.1645734522.jpg?c=2","alt":"Mononucleosomes, Recombinant, 199x601 DNA, Biotinylated"}],"date_added":"21st Oct 2020","pre_order":false,"show_cart_action":true,"has_options":true,"stock_level":null,"low_stock_level":null,"qty_in_cart":0,"custom_fields":[{"id":1187,"name":"Pack size","value":"50 µg"}],"num_reviews":null,"weight":{"formatted":"0.01 LBS","value":0.01},"demo":false,"price":{"without_tax":{"currency":"USD","formatted":"$575.00","value":575},"tax_label":"Sales Tax"},"add_to_wishlist_url":"/wishlist.php?action=add&product_id=792"},{"id":862,"sku":"16-0030","name":"Nucleosome, Recombinant Human, Acidic Patch Mutant H2AE92K Biotinylated","url":"https://www.epicypher.com/products/nucleosomes/mutant-nucleosomes/nucleosome-recombinant-human-acidic-patch-mutant-h2ae92k-biotinylated","availability":"","rating":null,"brand":{"name":null},"category":["Nucleosomes/Mutant Nucleosomes","Nucleosomes/Mutant Nucleosomes/Acidic Patch Nucleosomes"],"summary":"\n \n \n Species: Human\n \n \n Source: E. coli & synthetic DNA\n \n \n \n ","image":{"data":"https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-y9o92/images/stencil/{:size}/products/862/972/nucleosome-recombinant-human-acidic-patch-mutant-h2ae92k-biotinylated__90670.1645734564.jpg?c=2","alt":"Nucleosome, Recombinant Human, Acidic Patch Mutant H2AE92K Biotinylated"},"images":[{"data":"https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-y9o92/images/stencil/{:size}/products/862/972/nucleosome-recombinant-human-acidic-patch-mutant-h2ae92k-biotinylated__90670.1645734564.jpg?c=2","alt":"Nucleosome, Recombinant Human, Acidic Patch Mutant H2AE92K Biotinylated"}],"date_added":"21st May 2021","pre_order":false,"show_cart_action":true,"has_options":false,"stock_level":null,"low_stock_level":null,"qty_in_cart":0,"custom_fields":[{"id":805,"name":"Pack Size","value":"50 µg"}],"num_reviews":null,"weight":{"formatted":"0.00 LBS","value":0},"demo":false,"add_to_cart_url":"https://www.epicypher.com/cart.php?action=add&product_id=862","price":{"without_tax":{"currency":"USD","formatted":"$475.00","value":475},"tax_label":"Sales Tax"},"add_to_wishlist_url":"/wishlist.php?action=add&product_id=862"}],"shipping_messages":[],"rating":0,"meta_keywords":"acidic patch mutant, mutant nucleosome, mutant histone, H2AE92K, 16-2030","show_quantity_input":1,"title":"Acidic Patch Mutant H2AE92K Recombinant Nucleosome with Linker DNA, Biotinylated","gift_wrapping_available":false,"min_purchase_quantity":0,"customizations":[],"images":[{"data":"https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-y9o92/images/stencil/{:size}/products/705/1227/2021.05.05_acidic_patch_nuc_RGB_white_border_LS_icon_thumbnail_board_2__41959__47696.1717694541.png?c=2","alt":"Acidic Patch Mutant H2AE92K Recombinant Nucleosome with Linker DNA, Biotinylated"}]} Pack size: 50 µg
- Species: Human
- Source: E. coli & synthetic DNA
- Tag: Biotinylated
- Molecular Weight: 231,880 Da
Description
The acidic patch is a negatively charged region of the nucleosome surface that serves as a conserved interaction hub for neighboring nucleosomes and chromatin binding proteins, often via salt bridges with arginine anchors [1]. The acidic patch plays a critical role in chromatin condensation and chromatin remodeling [1-3]. Recombinant mononucleosomes containing acidic patch mutations can be used to study the biological functions of the acidic patch.
H2AE92K Recombinant Nucleosome with Linker DNA consists of 199 base pairs of DNA wrapped around an octamer core of histone proteins (two each of H2A, H2B, H3.1, and H4) to form a nucleosome, the basic repeating unit of chromatin. The 5’ biotin-TEG DNA consists of a core 147 bp 601 nucleosome assembly sequence [4] flanked by 26 bp linker sequences as underlined below. Histone H2A contains a glutamate-to-lysine (E-to-K) substitution at position 92 (H2AE92K). H2AE92 resides in the H2A C-terminal extension and mediates chromatin binding with factors such as H4-N-terminal tail, LANA, RCC1, IL-33, Sir3, HMGN2, and SMARCA5/SNF2h, an ATPase subunit of the ISWI family of chromatin remodeling complexes [1-3]. H2AE92K disrupts binding with SMARCB1/BAF47, a subunit of the SWI/SNF (BAF) family of chromatin remodeling complexes. These complexes serve a critical role in cell division, cell and tissue differentiation, and development, and SWI/SNF complex malfunction has been linked to over 20% of human cancers [5].
Validation Data
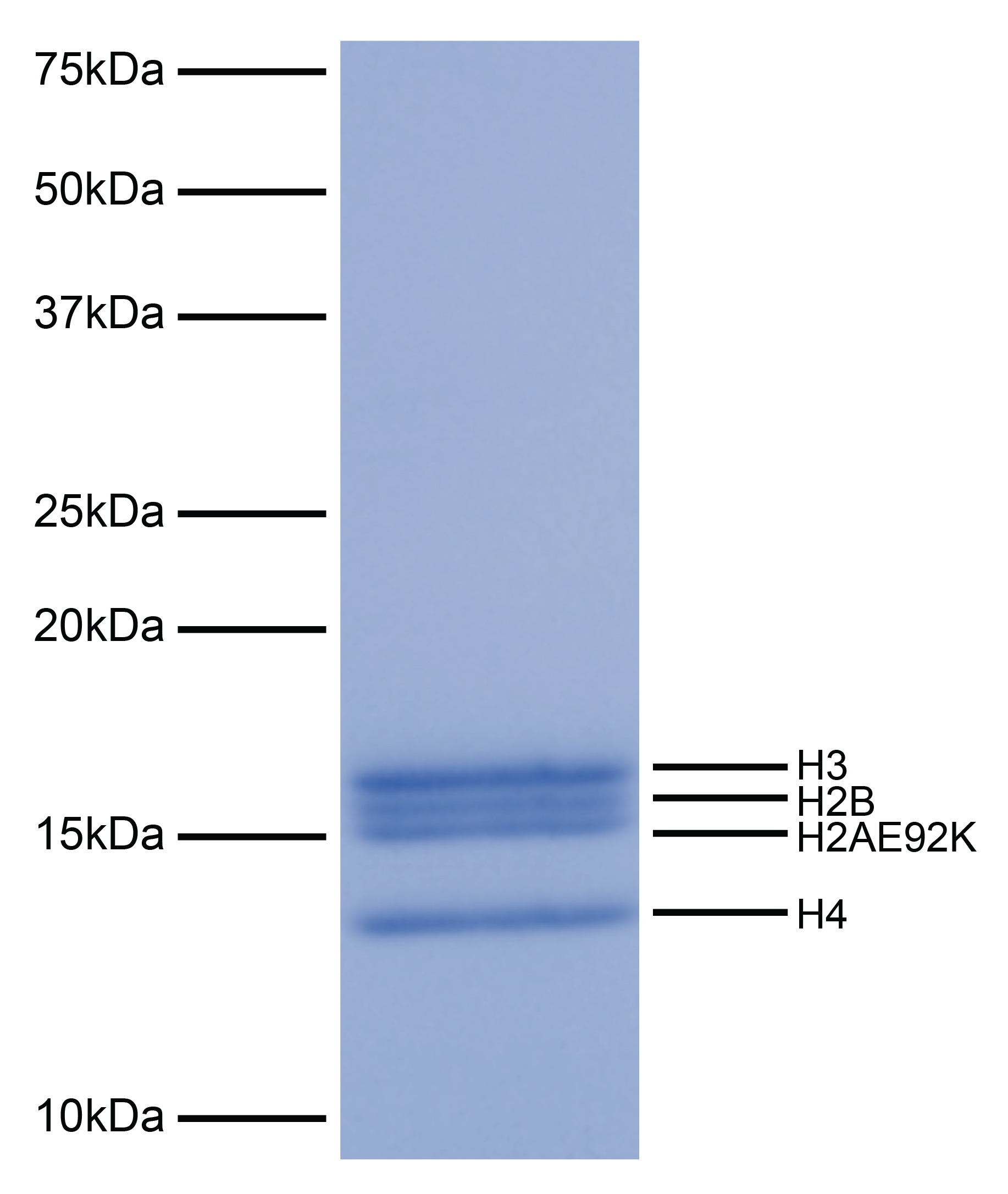
Figure 1: Protein gel gata
Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE gel of proteins in H2AE92K recombinant nucleosome (1 µg) demonstrates the
purity of histones in the preparation. Sizes of molecular weight markers and positions of the core
histones (H2AE92K, H2B, H3 and H4) are indicated.
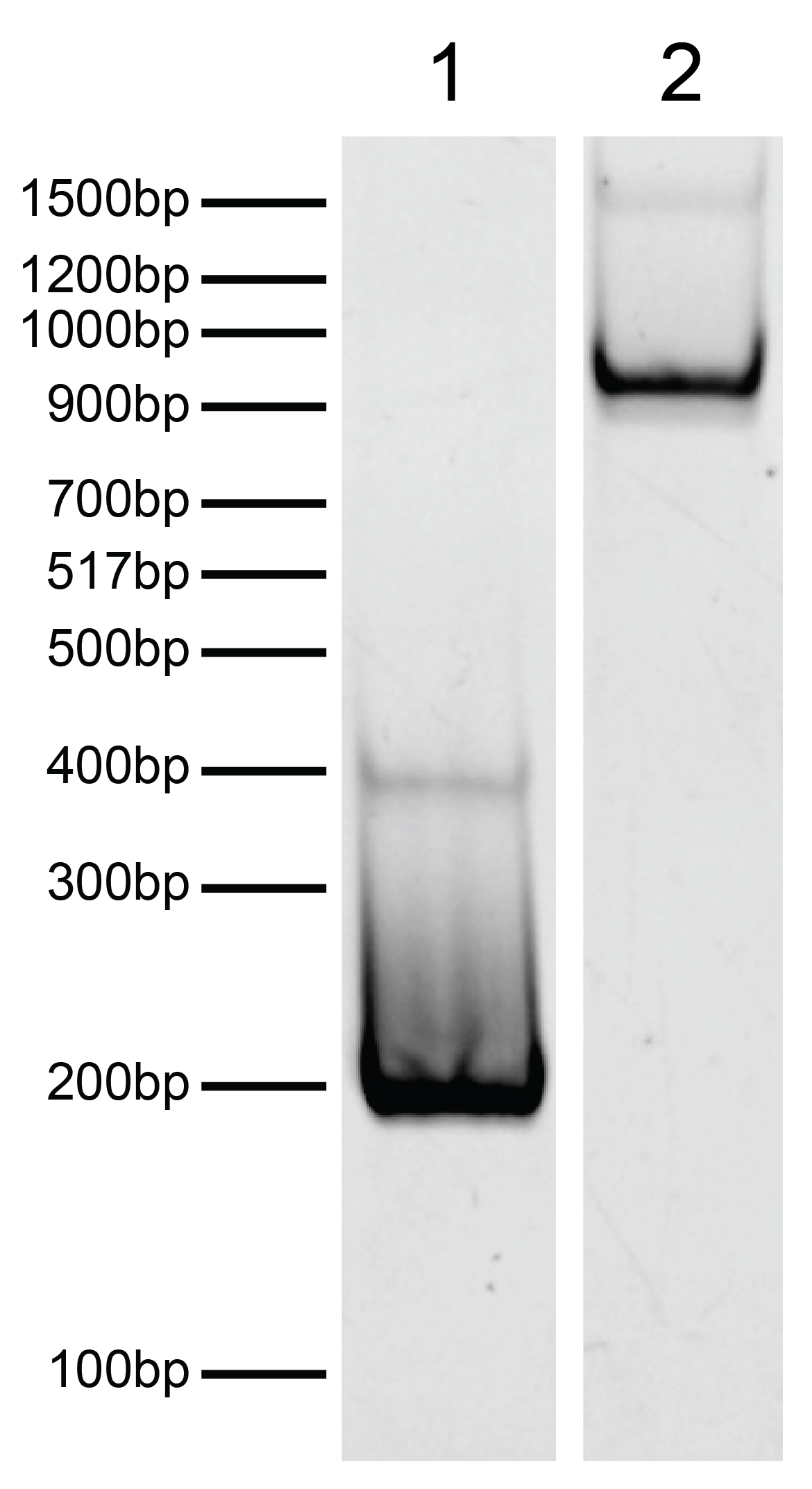
Figure 2: DNA gel data
H2AE92K recombinant nucleosome resolved by native PAGE and stained with ethidium bromide to
visualize DNA. Lane 1: Free DNA (EpiCypher 18-2044; 100 ng). Biotinylated DNA can dimerize (band at ~400 bp). Lane 2:
Intact H2AE92K recombinant nucleosomes (400 ng).
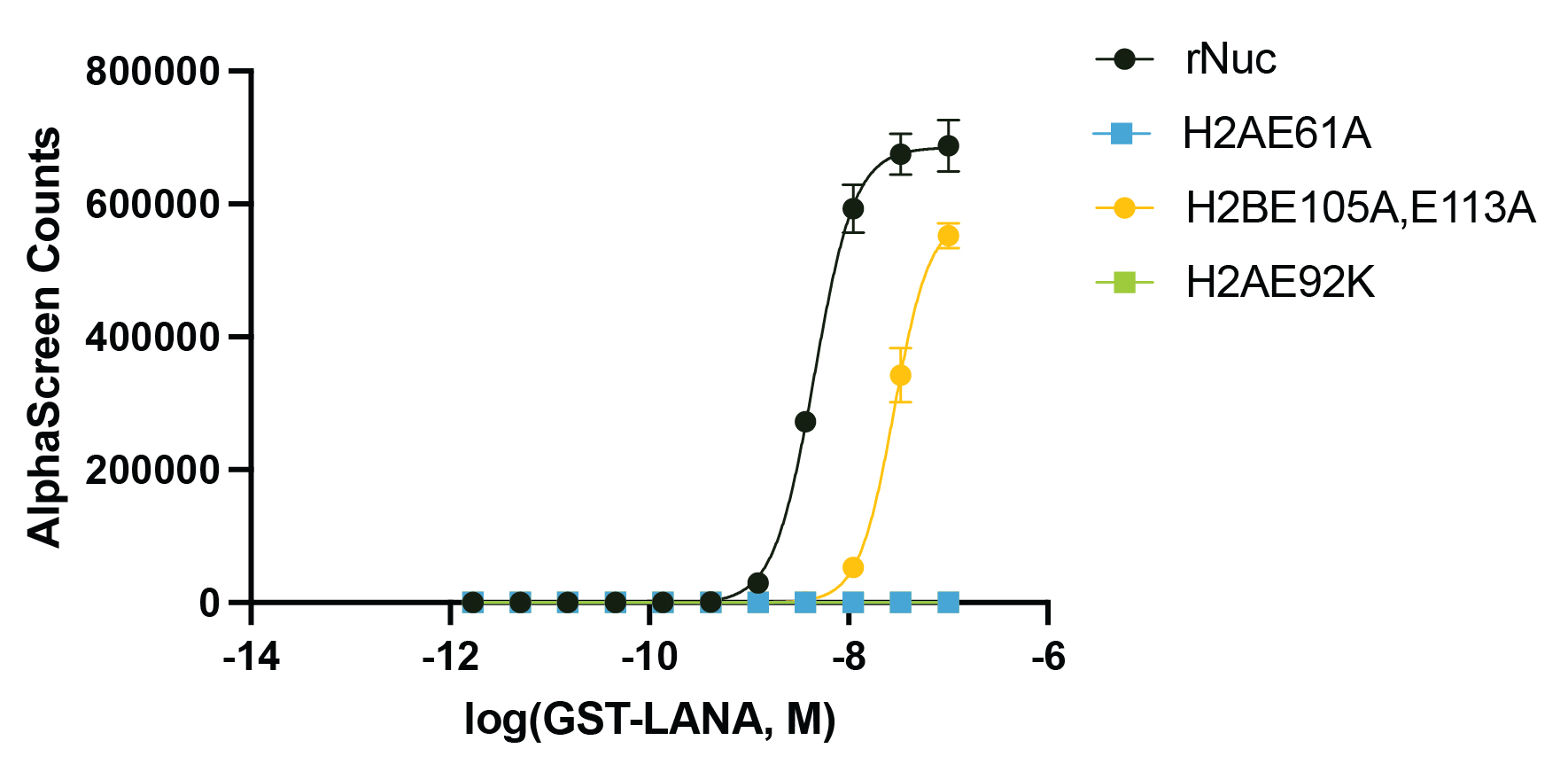
Figure 3: Functional binding assay
The presence of the acidic patch mutations disrupts LANA peptide binding to recombinant nucleosomes
(WT control, EpiCypher 16-2044; H2AE61A, EpiCypher 16-2029; H2AE92K, EpiCypher 16-2030;
H2BE105A,E113A, EpiCypher 16-2031). The binding of GST-tagged LANA peptide to biotinylated
recombinant nucleosomes was assessed by AlphaLISA assay using Streptavidin Donor Beads and
Glutathione Acceptor Beads (PerkinElmer). The presence of H2A acidic patch mutations completely
blocks LANA binding, while H2B mutations cause a decrease in LANA binding affinity.
Technical Information
Application Notes
H2AE92K mononucleosome is highly purified and suitable for a variety of applications to test the effect of acidic patch mutation on enzymatic activity or chromatin binding. The biotinylated DNA enables affinity binding applications. For a corresponding unmodified control, we recommend EpiCypher 16-2044.
DNA Sequence
5’Bio-TEG
GGACCCTATACGCGGCCGCCGAATTCCTGGAGAATCCCGGTCTGCAGGCCGCTCAATTGGTCGTAGACAGCTCTAGCACCGCTTAAACGCACGTACGCGCTGTCCCCCGCGTTTTAACCGCCAAGGGGATTACTCCCTAGTCTCCAGGCACGTGTCAGATATATACATCCTGTGGATCCGCCGGTCGCGAACAGCGACC3’
Gene & Protein Information
H2B - O60814 (alt. names: H2B K, HIRA-interacting protein 1)
H3.1 - P68431 (alt. names: H3, H3/a, H3/b, H3/c, H3/d)
H4 - P62805