![Heterotypic [H3K4me3 • H3K14ac] Recombinant Nucleosome, Biotinylated](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-y9o92/images/stencil/500x500/products/1167/1239/Heterotypic_Nuc_white__99511.1723235561.png?c=2)

Heterotypic [H3 • H3K4me3,K14ac] Recombinant Nucleosome, Biotinylated
{"url":"https://www.epicypher.com/products/nucleosomes/modified-designer-nucleosomes-dnucs/heterotypic-h3-h3k4me3-k14ac-recombinant-nucleosome-biotinylated","add_this":[{"service":"facebook","annotation":""},{"service":"email","annotation":""},{"service":"print","annotation":""},{"service":"twitter","annotation":""},{"service":"linkedin","annotation":""}],"gtin":null,"id":1166,"bulk_discount_rates":[],"can_purchase":true,"meta_description":"Heterotypic nucleosomes, also referred to as “asymmetric nucleosomes,” contain sister histones with distinct histone variants and/or post-translational modifications (PTMs). Heterotypic nucleosomes represent an additional layer of the histone code, acting as substrates for multivalent reader proteins, participating in PTM crosstalk mechanisms, and influencing reader protein binding affinity through varying local target concentration. Recombinant heterotypic nucleosomes are useful for studying chromatin dynamics and transcriptional regulation. Heterotypic [H3 • H3K4me3,K14ac] Recombinant Nucleosome, Biotinylated is a fully defined semi-synthetic nucleosome containing combinatorial PTMs in cis whereby one histone H3 is unmodified while the other is trimethylated at lysine four and acetylated at lysine 14. The NURF chromatin remodeling complex subunit BPTF engages heterotypic target PTMs in cis [H3 • H3K4me3,K14ac] as opposed to trans [H3K4me3 • H3K14ac] through tandem PHD finger and bromodomain (PHD-BD) reader interactions. ","category":["Nucleosomes","Nucleosomes/Modified Designer Nucleosomes (dNucs™)"],"AddThisServiceButtonMeta":"","main_image":{"data":"https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-y9o92/images/stencil/{:size}/products/1166/1238/Heterotypic_Nuc_white__67835.1723235454.png?c=2","alt":"Heterotypic [H3 • H3K4me3,K14ac] Recombinant Nucleosome, Biotinylated"},"add_to_wishlist_url":"/wishlist.php?action=add&product_id=1166","shipping":{"calculated":true},"num_reviews":0,"weight":"0.00 LBS","custom_fields":[{"id":"1331","name":"Pack Size","value":"25 µg"}],"sku":"16-0410","description":"<div class=\"product-general-info\">\n <ul class=\"product-general-info__list-left\">\n <li class=\"product-general-info__list-item\">\n <strong>Species: </strong>Human\n </li>\n <li class=\"product-general-info__list-item\">\n <strong>Source: </strong><i>E. coli</i> & synthetic DNA\n </li>\n </ul>\n <ul class=\"product-general-info__list-right\">\n <li class=\"product-general-info__list-item\">\n <strong>Tag: </strong>Biotinylated\n </li>\n <li class=\"product-general-info__list-item\">\n <strong>Molecular Weight: </strong>199,731 Da\n </li>\n </ul>\n</div>\n<div class=\"service_accordion product-droppdown\">\n <div class=\"container\">\n <div id=\"prodAccordion\">\n <div id=\"ProductDescription\" class=\"Block Panel current\">\n <h3 class=\"sub-title1\">Description</h3>\n <div class=\"ProductDescriptionContainer product-droppdown__section-description-specific\">\n <p>\n Heterotypic nucleosomes, also referred to as “asymmetric nucleosomes,” contain sister histones with distinct\n histone variants and/or post-translational modifications (PTMs). In homotypic nucleosomes, or “symmetric\n nucleosomes,” each pair of sister histones bears the same PTM, set of PTMs, or histone variant.\n Histone-modifying enzymes, chromatin remodelers, and histone chaperones differentially modify sister\n histones or exchange unique histone variants to form heterotypic nucleosomes. Heterotypic nucleosomes have\n been found at promoters of developmental genes in undifferentiated embryonic stem cells and transcription\n start sites (TSSs) of approximately half of the genes in budding yeast [1]. Heterotypic nucleosomes\n represent an additional layer of the histone code, acting as substrates for multivalent reader proteins,\n participating in PTM crosstalk mechanisms, and influencing reader protein binding affinity through varying\n local target concentration. Recombinant heterotypic nucleosomes are useful for studying chromatin dynamics\n and transcriptional regulation.\n </p>\n <p>\n Heterotypic [H3 • H3K4me3,K14ac] Recombinant Nucleosome, Biotinylated is a fully defined semi-synthetic\n nucleosome containing combinatorial PTMs in <em>cis</em> whereby one histone H3 is unmodified while the\n other is\n trimethylated at lysine four and acetylated at lysine 14. [H3 • H3K4me3,K14ac] nucleosome consists of 147\n base pairs of 601 sequence DNA [2] wrapped around an octamer of core histone proteins (two each of H2A, H2B,\n H3.2, and H4) to form a nucleosome, the basic repeating unit of chromatin. The DNA contains a 5’ biotin-TEG\n group, and histone H3.2 has a Cys to Ala substitution at position 110. The NURF chromatin remodeling complex\n subunit BPTF engages heterotypic target PTMs in <em>cis</em> [H3 • H3K4me3,K14ac] as opposed to\n <em>trans</em> [H3K4me3 •\n H3K14ac] through tandem PHD finger and bromodomain (PHD-BD) reader interactions [3].\n </p>\n </div>\n </div>\n </div>\n <div id=\"prodAccordion\">\n <div id=\"ProductDescription\" class=\"Block Panel current\">\n <h3 class=\"sub-title1\">Validation Data</h3>\n <div class=\"ProductDescriptionContainer product-droppdown__section-description-specific\">\n <section class=\"image-picker\">\n <div class=\"image-picker__left\">\n <div class=\"image-picker__main-content_active image-picker__main-content\">\n <div class=\"image-picker__header-content\">\n <button class=\"image-picker__left-arrow\">\n <svg class=\"image-picker__svg-left\" width=\"24\" height=\"24\" viewBox=\"0 0 24 24\">\n <path d=\"M16.67 0l2.83 2.829-9.339 9.175 9.339 9.167-2.83 2.829-12.17-11.996z\" />\n </svg>\n </button>\n <a href=\"/content/images/products/nucleosomes/16-0410-protein-gel.jpeg\" target=\"_blank\"\n class=\"image-picker__main-image-link\"><img alt=\"16-0410-protein-gel\"\n src=\"/content/images/products/nucleosomes/16-0410-protein-gel.jpeg\"\n class=\"image-picker__main-image\" />\n <span class=\"image-picker__main-image-caption\">(Click to enlarge)</span></a>\n <button class=\"image-picker__right-arrow\">\n <svg class=\"image-picker__svg-right\" width=\"24\" height=\"24\" viewBox=\"0 0 24 24\">\n <path d=\"M7.33 24l-2.83-2.829 9.339-9.175-9.339-9.167 2.83-2.829 12.17 11.996z\" />\n </svg>\n </button>\n </div>\n <p>\n <span class=\"image-picker__span-content\"><strong>Figure 1: Protein gel data</strong><br />\n Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE gel of proteins in heterotypic [H3 • H3K4me3,K14ac] nucleosome (1 µg)\n demonstrates the purity of histones in the preparation. Sizes of molecular weight markers and\n positions of the core histones (H2A, H2B, H3 • H3K4me3,K14ac, and H4) are indicated.\n </span>\n </p>\n </div>\n <div class=\"image-picker__main-content\">\n <div class=\"image-picker__header-content\">\n <button class=\"image-picker__left-arrow\">\n <svg class=\"image-picker__svg-left\" width=\"24\" height=\"24\" viewBox=\"0 0 24 24\">\n <path d=\"M16.67 0l2.83 2.829-9.339 9.175 9.339 9.167-2.83 2.829-12.17-11.996z\" />\n </svg>\n </button>\n <a href=\"/content/images/products/nucleosomes/16-0410-dna-gel.jpeg\" target=\"_blank\"\n class=\"image-picker__main-image-link\"><img alt=\"16-0410-dna-gel\"\n src=\"/content/images/products/nucleosomes/16-0410-dna-gel.jpeg\"\n class=\"image-picker__main-image\" />\n <span class=\"image-picker__main-image-caption\">(Click to enlarge)</span></a>\n <button class=\"image-picker__right-arrow\">\n <svg class=\"image-picker__svg-right\" width=\"24\" height=\"24\" viewBox=\"0 0 24 24\">\n <path d=\"M7.33 24l-2.83-2.829 9.339-9.175-9.339-9.167 2.83-2.829 12.17 11.996z\" />\n </svg>\n </button>\n </div>\n <p>\n <span class=\"image-picker__span-content\"><strong>Figure 2: DNA gel data </strong><br />\n Heterotypic [H3 • H3K4me3,K14ac] nucleosome resolved via native PAGE and stained with ethidium\n bromide to visualize DNA. Both lanes are from the same gel. <b>Lane 1</b>: Free DNA (EpiCypher <a\n href=\"/products/nucleosomes/nucleosome-assembly-601-sequence-dna-biotinylated\"\n target=\"_blank\">18-0005</a>; 75 ng). Free\n DNA is over 95% pure by densitometry. <b>Lane 2</b>: Intact heterotypic [H3 • H3K4me3,K14ac]\n nucleosomes (400 ng).\n </span>\n </p>\n </div>\n <div class=\"image-picker__main-content\">\n <div class=\"image-picker__header-content\">\n <button class=\"image-picker__left-arrow\">\n <svg class=\"image-picker__svg-left\" width=\"24\" height=\"24\" viewBox=\"0 0 24 24\">\n <path d=\"M16.67 0l2.83 2.829-9.339 9.175 9.339 9.167-2.83 2.829-12.17-11.996z\" />\n </svg>\n </button>\n <a href=\"/content/images/products/nucleosomes/16-0410-luminex-multiplexed.jpeg\" target=\"_blank\"\n class=\"image-picker__main-image-link\">\n <img alt=\"16-0410-luminex-multiplexed\"\n src=\"/content/images/products/nucleosomes/16-0410-luminex-multiplexed.jpeg\"\n class=\"image-picker__main-image\" />\n <span class=\"image-picker__main-image-caption\">(Click to enlarge)</span>\n </a>\n <button class=\"image-picker__right-arrow\">\n <svg class=\"image-picker__svg-right\" width=\"24\" height=\"24\" viewBox=\"0 0 24 24\">\n <path d=\"M7.33 24l-2.83-2.829 9.339-9.175-9.339-9.167 2.83-2.829 12.17 11.996z\" />\n </svg>\n </button>\n </div>\n <p>\n <span class=\"image-picker__span-content\">\n <strong>Figure 3: Luminex multiplexed specificity profiling</strong><br />\n Heterotypic [H3 • H3K4me3,K14ac] nucleosome was assessed using a Luminex® based approach. The panel\n comprises biotinylated designer nucleosomes individually coupled to color-coded Luminex MagPlex®\n beads. Histone antibody (EMD Millipore MAB3422), DNA antibody (EMD Millipore MAB030), H3K4me3\n antibody (EpiCypher <a\n href=\"/products/antibodies/h3k4me3-antibody-snap-certified-for-cut-run-and-cut-tag\"\n target=\"_blank\">13-0060</a>), and H3K14ac antibody (ThermoFisher MA5-32814) were added (x-axis),\n and a second layer of anti-IgG*Phycoerythrin (PE; BioLegend 406421 for anti-rabbit IgG or BioLegend\n 405307 for anti-mouse IgG) was used for detection. Data were generated using a Luminex FlexMAP 3D®.\n Histone and DNA antibodies bind nucleosomes in the panel equivalently, as expected. H3K4me3 antibody\n and H3K14ac antibody bind heterotypic [H3 • H3K4me3,K14ac] nucleosomes at reduced strength in\n comparison to homotypic H3K4me3 (EpiCypher <a\n href=\"/products/nucleosomes/nucleosome-recombinant-human-h3k4me3-dnuc-biotinylated\"\n target=\"_blank\">16-0316</a>) and H3K14ac (EpiCypher\n <a href=\"/products/nucleosomes/nucleosome-recombinant-human-h3k14ac-dnuc-biotinylated\"\n target=\"_blank\">16-0343</a>) nucleosomes.\n </span>\n </p>\n </div>\n </div>\n <aside class=\"image-picker__right\">\n <div class=\"image-picker__gallery\">\n <img alt=\"16-0410-protein-gel\" src=\"/content/images/products/nucleosomes/16-0410-protein-gel.jpeg\"\n width=\"200\" class=\"image-picker__side-image image-picker__side-image_active\" role=\"button\" />\n <img alt=\"16-0410-dna-gel\" src=\"/content/images/products/nucleosomes/16-0410-dna-gel.jpeg\"\n class=\"image-picker__side-image\" role=\"button\" />\n <img alt=\"16-0410-luminex-multiplexed\"\n src=\"/content/images/products/nucleosomes/16-0410-luminex-multiplexed.jpeg\"\n class=\"image-picker__side-image\" role=\"button\" />\n </div>\n </aside>\n </section>\n </div>\n </div>\n </div>\n <div id=\"prodAccordion\">\n <div id=\"ProductDescription\" class=\"Block Panel\">\n <h3 class=\"sub-title1\">Technical Information</h3>\n <div class=\"ProductDescriptionContainer product-droppdown__section-description\">\n <div class=\"product-tech-info\">\n <div class=\"product-tech-info__line-item\">\n <div class=\"product-tech-info__line-item-left\">\n <b>Storage</b>\n </div>\n <div class=\"product-tech-info__line-item-right\">\n Stable for six months at -80°C from date of receipt. For best\n results, aliquot and avoid freeze/thaws.\n </div>\n </div>\n <div class=\"product-tech-info__line-item\">\n <div class=\"product-tech-info__line-item-left\">\n <b>Formulation</b>\n </div>\n <div class=\"product-tech-info__line-item-right\">\n 10 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.5, 25 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, 2 mM DTT, 20%\n glycerol (13.6 µg protein, 25 µg DNA + protein).\n </div>\n </div>\n </div>\n </div>\n </div>\n </div>\n <div id=\"prodAccordion\">\n <div id=\"ProductDescription\" class=\"Block Panel\">\n <h3 class=\"sub-title1\">Application Notes</h3>\n <div class=\"ProductDescriptionContainer product-droppdown__section-description\">\n <p>\n Heterotypic [H3 • H3K4me3,K14ac] nucleosome is highly purified and suitable for a variety of applications,\n including use as a substrate in enzyme assays, high-throughput screening and inhibitor testing, chromatin\n binding studies, protein-protein interaction assays, structural studies, and in effector protein binding\n experiments. Trace amounts of TEV protease may be present (less than 5% of the preparation by densitometry,\n <b>Figure 1</b>). For a corresponding homotypic control, we recommend EpiCypher <a\n href=\"/products/nucleosomes/nucleosome-recombinant-human-h3k4me3-dnuc-biotinylated\">16-0316</a> and/or\n EpiCypher <a href=\"/products/nucleosomes/nucleosome-recombinant-human-h3k14ac-dnuc-biotinylated\"\n target=\"_blank\">16-0343</a>.\n </p>\n </div>\n </div>\n </div>\n <div id=\"prodAccordion\">\n <div id=\"ProductDescription\" class=\"Block Panel\">\n <h3 class=\"sub-title1\">Gene & Protein Information</h3>\n <div class=\"ProductDescriptionContainer product-droppdown__section-description\">\n <div class=\"product-tech-info\">\n <div class=\"product-tech-info__line-item\">\n <div class=\"product-tech-info__line-item-left\">\n <b>UniProt ID</b>\n </div>\n <div class=\"product-tech-info__line-item-right\">\n H2A - P04908 (alt. names: H2A type 1-B/E, H2A.2, H2A/a, H2A/m)<br />\n H2B - O60814 (alt. names: H2B K, HIRA-interacting protein 1)<br />\n H3.2 - Q71DI3<br />\n H4 - P62805\n </div>\n </div>\n </div>\n </div>\n </div>\n </div>\n <div id=\"prodAccordion\">\n <div id=\"ProductDescription\" class=\"Block Panel\">\n <h3 class=\"sub-title1\">References</h3>\n <div class=\"ProductDescriptionContainer product-droppdown__section-description\">\n <strong>Background References:</strong>\n <br />\n [1] Valsakumar & Voigt. <em>Biochem. Soc. Trans.</em> (2024). PMID:\n <a href=\"https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38778762/\" target=\"_blank\"\n title=\"Nucleosomal asymmetry: a novel mechanism to regulate nucleosome function\">38778762</a><br />\n [2] Lowary & Widom <em>J. Mol. Biol.</em> (1998). PMID:\n <a href=\"https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9514715/\" target=\"_blank\"\n title=\"New DNA sequence rules for high affinity binding to histone octamer and sequence-directed nucleosome positioning\">9514715</a><br />\n [3] Marunde et al. <em>eLife</em> (2024). PMID:\n <a href=\"https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38319148/\" target=\"_blank\"\n title=\"Nucleosome conformation dictates the histone code\">38319148</a><br />\n </div>\n </div>\n </div>\n <div id=\"prodAccordion\">\n <div id=\"ProductDescription\" class=\"Block Panel\">\n <h3 class=\"sub-title1\">Documents & Resources</h3>\n <div class=\"ProductDescriptionContainer product-droppdown__section-description\">\n <div class=\"product-documents\">\n <a href=\"/content/documents/tds/16-0410.pdf\" target=\"_blank\" class=\"product-documents__link\">\n <svg version=\"1.1\" id=\"Layer_1\" xmlns=\"http://www.w3.org/2000/svg\"\n xmlns:xlink=\"http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink\" x=\"0px\" y=\"0px\" viewBox=\"0 0 228 240\"\n style=\"enable-background: new 0 0 228 240\" xml:space=\"preserve\" class=\"product-documents__icon\"\n alt=\"16-0410 Datasheet\">\n <g>\n <path class=\"product-documents__svg-pdf\"\n d=\"M191.92,68.77l-47.69-47.69c-1.33-1.33-3.12-2.08-5.01-2.08H45.09C41.17,19,38,22.17,38,26.09v184.36\n c0,3.92,3.17,7.09,7.09,7.09h141.82c3.92,0,7.09-3.17,7.09-7.09V73.8C194,71.92,193.25,70.1,191.92,68.77z M177.65,77.06h-41.7\n v-41.7L177.65,77.06z M178.05,201.59H53.95V34.95h66.92v47.86c0,5.14,4.17,9.31,9.31,9.31h47.86V201.59z\" />\n </g>\n <rect x=\"20\" y=\"112\" class=\"product-documents__svg-background\" width=\"146\" height=\"76\" />\n <g>\n <path class=\"product-documents__svg-pdf\" d=\"M23.83,125.68h22.36c5.29,0,9.41,1.33,12.35,4c2.94,2.67,4.42,6.39,4.42,11.18c0,4.78-1.47,8.51-4.42,11.18\n c-2.94,2.67-7.06,4-12.35,4H34.59v18.29H23.83V125.68z M44.81,147.9c5.38,0,8.07-2.32,8.07-6.97c0-2.39-0.67-4.16-2-5.31\n c-1.33-1.15-3.36-1.73-6.07-1.73H34.59v14.01H44.81z\" />\n <path class=\"product-documents__svg-pdf\" d=\"M69.92,125.68h18.91c5.29,0,9.84,0.97,13.66,2.9c3.82,1.93,6.74,4.72,8.76,8.35\n c2.02,3.63,3.04,7.98,3.04,13.04c0,5.06-1,9.42-3,13.08c-2,3.66-4.91,6.45-8.73,8.38c-3.82,1.93-8.4,2.9-13.73,2.9H69.92V125.68z\n M88.07,165.63c10.35,0,15.52-5.22,15.52-15.66c0-10.4-5.17-15.59-15.52-15.59h-7.38v31.26H88.07z\" />\n <path class=\"product-documents__svg-pdf\"\n d=\"M122.57,125.68h32.84v8.49h-22.22v11.18h20.84v8.49h-20.84v20.49h-10.63V125.68z\" />\n </g>\n </svg>\n <span class=\"product-documents__info\">Technical Datasheet</span>\n </a>\n </div>\n </div>\n </div>\n </div>\n </div>\n</div>","tags":[],"warranty":"","price":{"without_tax":{"formatted":"$525.00","value":525,"currency":"USD"},"tax_label":"Sales Tax"},"detail_messages":"","availability":"","page_title":"Heterotypic [H3 • H3K4me3,K14ac] Recombinant Nucleosome, Biotinylated","cart_url":"https://www.epicypher.com/cart.php","max_purchase_quantity":0,"mpn":null,"upc":null,"options":[],"related_products":[{"id":1164,"sku":"16-0408","name":"Heterotypic [H3 • H3K4me3] Recombinant Nucleosome, Biotinylated","url":"https://www.epicypher.com/products/nucleosomes/modified-designer-nucleosomes-dnucs/heterotypic-h3-h3k4me3-recombinant-nucleosome-biotinylated","availability":"","rating":null,"brand":{"name":null},"category":["Nucleosomes","Nucleosomes/Modified Designer Nucleosomes (dNucs™)"],"summary":"\n \n \n Species: Human\n \n \n Source: E. coli & synthetic DNA\n \n \n \n ","image":{"data":"https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-y9o92/images/stencil/{:size}/products/1164/1236/Heterotypic_Nuc_white__46729.1723235178.png?c=2","alt":"Heterotypic [H3 • H3K4me3] Recombinant Nucleosome, Biotinylated"},"images":[{"data":"https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-y9o92/images/stencil/{:size}/products/1164/1236/Heterotypic_Nuc_white__46729.1723235178.png?c=2","alt":"Heterotypic [H3 • H3K4me3] Recombinant Nucleosome, Biotinylated"}],"date_added":"9th Aug 2024","pre_order":false,"show_cart_action":true,"has_options":false,"stock_level":null,"low_stock_level":null,"qty_in_cart":0,"custom_fields":[{"id":1329,"name":"Pack Size","value":"25 µg"}],"num_reviews":null,"weight":{"formatted":"0.00 LBS","value":0},"demo":false,"add_to_cart_url":"https://www.epicypher.com/cart.php?action=add&product_id=1164","price":{"without_tax":{"currency":"USD","formatted":"$525.00","value":525},"tax_label":"Sales Tax"},"add_to_wishlist_url":"/wishlist.php?action=add&product_id=1164"},{"id":1165,"sku":"16-0409","name":"Heterotypic [H3 • H3K14ac] Recombinant Nucleosome, Biotinylated","url":"https://www.epicypher.com/products/nucleosomes/modified-designer-nucleosomes-dnucs/heterotypic-h3-h3k14ac-recombinant-nucleosome-biotinylated","availability":"","rating":null,"brand":{"name":null},"category":["Nucleosomes","Nucleosomes/Modified Designer Nucleosomes (dNucs™)"],"summary":"\n \n \n Species: Human\n \n \n Source: E. coli & synthetic DNA\n \n \n \n ","image":{"data":"https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-y9o92/images/stencil/{:size}/products/1165/1237/Heterotypic_Nuc_white__35995.1723235305.png?c=2","alt":"Heterotypic [H3 • H3K14ac] Recombinant Nucleosome, Biotinylated"},"images":[{"data":"https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-y9o92/images/stencil/{:size}/products/1165/1237/Heterotypic_Nuc_white__35995.1723235305.png?c=2","alt":"Heterotypic [H3 • H3K14ac] Recombinant Nucleosome, Biotinylated"}],"date_added":"9th Aug 2024","pre_order":false,"show_cart_action":true,"has_options":false,"stock_level":null,"low_stock_level":null,"qty_in_cart":0,"custom_fields":[{"id":1330,"name":"Pack Size","value":"25 µg"}],"num_reviews":null,"weight":{"formatted":"0.00 LBS","value":0},"demo":false,"add_to_cart_url":"https://www.epicypher.com/cart.php?action=add&product_id=1165","price":{"without_tax":{"currency":"USD","formatted":"$525.00","value":525},"tax_label":"Sales Tax"},"add_to_wishlist_url":"/wishlist.php?action=add&product_id=1165"},{"id":1167,"sku":"16-0411","name":"Heterotypic [H3K4me3 • H3K14ac] Recombinant Nucleosome, Biotinylated","url":"https://www.epicypher.com/products/nucleosomes/modified-designer-nucleosomes-dnucs/heterotypic-h3k4me3-h3k14ac-recombinant-nucleosome-biotinylated","availability":"","rating":null,"brand":{"name":null},"category":["Nucleosomes","Nucleosomes/Modified Designer Nucleosomes (dNucs™)"],"summary":"\n \n \n Species: Human\n \n \n Source: E. coli & synthetic DNA\n \n \n \n ","image":{"data":"https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-y9o92/images/stencil/{:size}/products/1167/1239/Heterotypic_Nuc_white__99511.1723235561.png?c=2","alt":"Heterotypic [H3K4me3 • H3K14ac] Recombinant Nucleosome, Biotinylated"},"images":[{"data":"https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-y9o92/images/stencil/{:size}/products/1167/1239/Heterotypic_Nuc_white__99511.1723235561.png?c=2","alt":"Heterotypic [H3K4me3 • H3K14ac] Recombinant Nucleosome, Biotinylated"}],"date_added":"9th Aug 2024","pre_order":false,"show_cart_action":true,"has_options":false,"stock_level":null,"low_stock_level":null,"qty_in_cart":0,"custom_fields":[{"id":1332,"name":"Pack Size","value":"25 µg"}],"num_reviews":null,"weight":{"formatted":"0.00 LBS","value":0},"demo":false,"add_to_cart_url":"https://www.epicypher.com/cart.php?action=add&product_id=1167","price":{"without_tax":{"currency":"USD","formatted":"$525.00","value":525},"tax_label":"Sales Tax"},"add_to_wishlist_url":"/wishlist.php?action=add&product_id=1167"},{"id":1168,"sku":"16-0415","name":"Heterotypic [H3K4me3 • H3K9,14,18ac] Recombinant Nucleosome, Biotinylated","url":"https://www.epicypher.com/products/nucleosomes/modified-designer-nucleosomes-dnucs/heterotypic-h3k4me3-h3k9-14-18ac-recombinant-nucleosome-biotinylated","availability":"","rating":null,"brand":{"name":null},"category":["Nucleosomes","Nucleosomes/Modified Designer Nucleosomes (dNucs™)"],"summary":"\n \n \n Species: Human\n \n \n Source: E. coli & synthetic DNA\n \n \n \n ","image":{"data":"https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-y9o92/images/stencil/{:size}/products/1168/1240/Heterotypic_Nuc_white__85489.1723235678.png?c=2","alt":"Heterotypic [H3K4me3 • H3K9,14,18ac] Recombinant Nucleosome, Biotinylated"},"images":[{"data":"https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-y9o92/images/stencil/{:size}/products/1168/1240/Heterotypic_Nuc_white__85489.1723235678.png?c=2","alt":"Heterotypic [H3K4me3 • H3K9,14,18ac] Recombinant Nucleosome, Biotinylated"}],"date_added":"9th Aug 2024","pre_order":false,"show_cart_action":true,"has_options":false,"stock_level":null,"low_stock_level":null,"qty_in_cart":0,"custom_fields":[{"id":1333,"name":"Pack Size","value":"25 µg"}],"num_reviews":null,"weight":{"formatted":"0.00 LBS","value":0},"demo":false,"add_to_cart_url":"https://www.epicypher.com/cart.php?action=add&product_id=1168","price":{"without_tax":{"currency":"USD","formatted":"$525.00","value":525},"tax_label":"Sales Tax"},"add_to_wishlist_url":"/wishlist.php?action=add&product_id=1168"},{"id":296,"sku":null,"name":"Nucleosome, Recombinant Human, H3K4me3 dNuc, Biotinylated","url":"https://www.epicypher.com/products/nucleosomes/nucleosome-recombinant-human-h3k4me3-dnuc-biotinylated","availability":"","rating":null,"brand":{"name":null},"category":["Nucleosomes","Nucleosomes/Modified Designer Nucleosomes (dNucs™)","Nucleosomes/Modified Designer Nucleosomes (dNucs™)/dNuc - Smaller Pack Size Available"],"summary":"\n \n \n Species: Human\n \n \n Source: E. coli & synthetic DNA\n \n \n \n ","image":{"data":"https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-y9o92/images/stencil/{:size}/products/296/283/dNucs__33084.1569012494.png?c=2","alt":"Nucleosome, Recombinant Human, H3K4me3 dNuc, Biotinylated"},"images":[{"data":"https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-y9o92/images/stencil/{:size}/products/296/275/3_Nucleosome__08589.1569012494.jpg?c=2","alt":"Nucleosome, Recombinant Human, H3K4me3 dNuc, Biotinylated"},{"data":"https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-y9o92/images/stencil/{:size}/products/296/283/dNucs__33084.1569012494.png?c=2","alt":"Nucleosome, Recombinant Human, H3K4me3 dNuc, Biotinylated"}],"date_added":"11th May 2016","pre_order":false,"show_cart_action":true,"has_options":true,"stock_level":null,"low_stock_level":null,"qty_in_cart":0,"custom_fields":null,"num_reviews":null,"weight":{"formatted":"0.01 LBS","value":0.01},"demo":false,"price":{"without_tax":{"currency":"USD","formatted":"$575.00","value":575},"price_range":{"min":{"without_tax":{"currency":"USD","formatted":"$295.00","value":295},"tax_label":"Sales Tax"},"max":{"without_tax":{"currency":"USD","formatted":"$575.00","value":575},"tax_label":"Sales Tax"}},"tax_label":"Sales Tax"},"add_to_wishlist_url":"/wishlist.php?action=add&product_id=296"},{"id":378,"sku":"16-0343","name":"Nucleosome, Recombinant Human, H3K14ac dNuc, Biotinylated","url":"https://www.epicypher.com/products/nucleosomes/nucleosome-recombinant-human-h3k14ac-dnuc-biotinylated","availability":"","rating":null,"brand":{"name":null},"category":["Nucleosomes","Nucleosomes/Modified Designer Nucleosomes (dNucs™)"],"summary":" \n","image":{"data":"https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-y9o92/images/stencil/{:size}/products/378/315/Recombinant_nucleosome__88778.1582226101.png?c=2","alt":"Nucleosome, Recombinant Human, H3K14ac dNuc, Biotinylated"},"images":[{"data":"https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-y9o92/images/stencil/{:size}/products/378/315/Recombinant_nucleosome__88778.1582226101.png?c=2","alt":"Nucleosome, Recombinant Human, H3K14ac dNuc, Biotinylated"}],"date_added":"1st Aug 2017","pre_order":false,"show_cart_action":true,"has_options":false,"stock_level":null,"low_stock_level":null,"qty_in_cart":0,"custom_fields":[{"id":206,"name":"Pack Size","value":"50 μg"}],"num_reviews":null,"weight":{"formatted":"0.01 LBS","value":0.01},"demo":false,"add_to_cart_url":"https://www.epicypher.com/cart.php?action=add&product_id=378","price":{"without_tax":{"currency":"USD","formatted":"$575.00","value":575},"tax_label":"Sales Tax"},"add_to_wishlist_url":"/wishlist.php?action=add&product_id=378"}],"shipping_messages":[],"rating":0,"meta_keywords":"H3 • H3K4me3K14ac, H3/H3K4me3K14ac, H3K4me3, H3K14ac, heterotypic nucleosome, heterotypic nucleosomes, asymmetric nucleosome, asymmetric nucleosomes, designer nucleosome, dNuc, nucleosome, nucleosomes","show_quantity_input":1,"title":"Heterotypic [H3 • H3K4me3,K14ac] Recombinant Nucleosome, Biotinylated","gift_wrapping_available":false,"min_purchase_quantity":0,"customizations":[],"images":[{"data":"https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-y9o92/images/stencil/{:size}/products/1166/1238/Heterotypic_Nuc_white__67835.1723235454.png?c=2","alt":"Heterotypic [H3 • H3K4me3,K14ac] Recombinant Nucleosome, Biotinylated"}]} Pack Size: 25 µg
- Species: Human
- Source: E. coli & synthetic DNA
- Tag: Biotinylated
- Molecular Weight: 199,731 Da
Description
Heterotypic nucleosomes, also referred to as “asymmetric nucleosomes,” contain sister histones with distinct histone variants and/or post-translational modifications (PTMs). In homotypic nucleosomes, or “symmetric nucleosomes,” each pair of sister histones bears the same PTM, set of PTMs, or histone variant. Histone-modifying enzymes, chromatin remodelers, and histone chaperones differentially modify sister histones or exchange unique histone variants to form heterotypic nucleosomes. Heterotypic nucleosomes have been found at promoters of developmental genes in undifferentiated embryonic stem cells and transcription start sites (TSSs) of approximately half of the genes in budding yeast [1]. Heterotypic nucleosomes represent an additional layer of the histone code, acting as substrates for multivalent reader proteins, participating in PTM crosstalk mechanisms, and influencing reader protein binding affinity through varying local target concentration. Recombinant heterotypic nucleosomes are useful for studying chromatin dynamics and transcriptional regulation.
Heterotypic [H3 • H3K4me3,K14ac] Recombinant Nucleosome, Biotinylated is a fully defined semi-synthetic nucleosome containing combinatorial PTMs in cis whereby one histone H3 is unmodified while the other is trimethylated at lysine four and acetylated at lysine 14. [H3 • H3K4me3,K14ac] nucleosome consists of 147 base pairs of 601 sequence DNA [2] wrapped around an octamer of core histone proteins (two each of H2A, H2B, H3.2, and H4) to form a nucleosome, the basic repeating unit of chromatin. The DNA contains a 5’ biotin-TEG group, and histone H3.2 has a Cys to Ala substitution at position 110. The NURF chromatin remodeling complex subunit BPTF engages heterotypic target PTMs in cis [H3 • H3K4me3,K14ac] as opposed to trans [H3K4me3 • H3K14ac] through tandem PHD finger and bromodomain (PHD-BD) reader interactions [3].
Validation Data
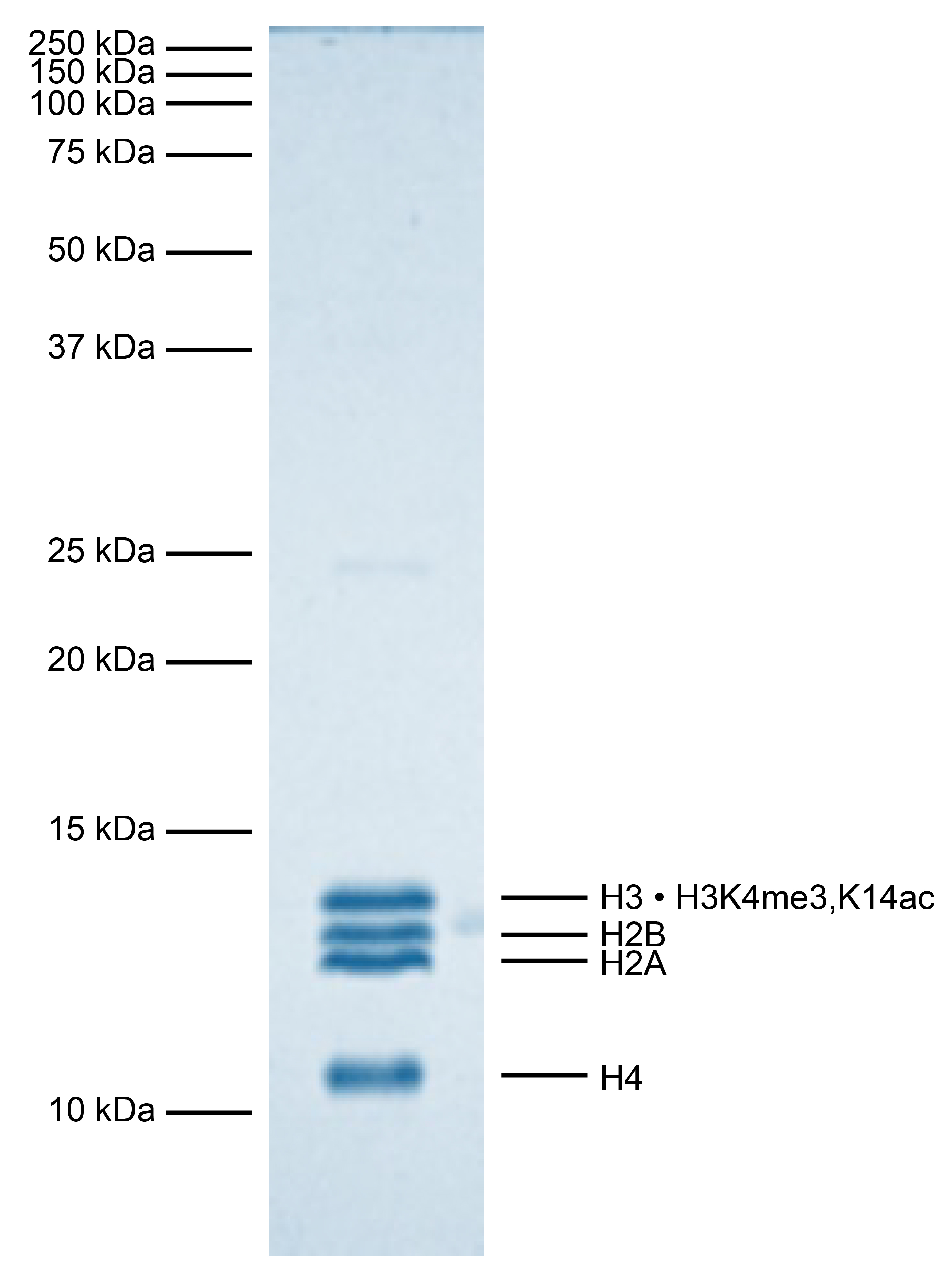
Figure 1: Protein gel data
Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE gel of proteins in heterotypic [H3 • H3K4me3,K14ac] nucleosome (1 µg)
demonstrates the purity of histones in the preparation. Sizes of molecular weight markers and
positions of the core histones (H2A, H2B, H3 • H3K4me3,K14ac, and H4) are indicated.
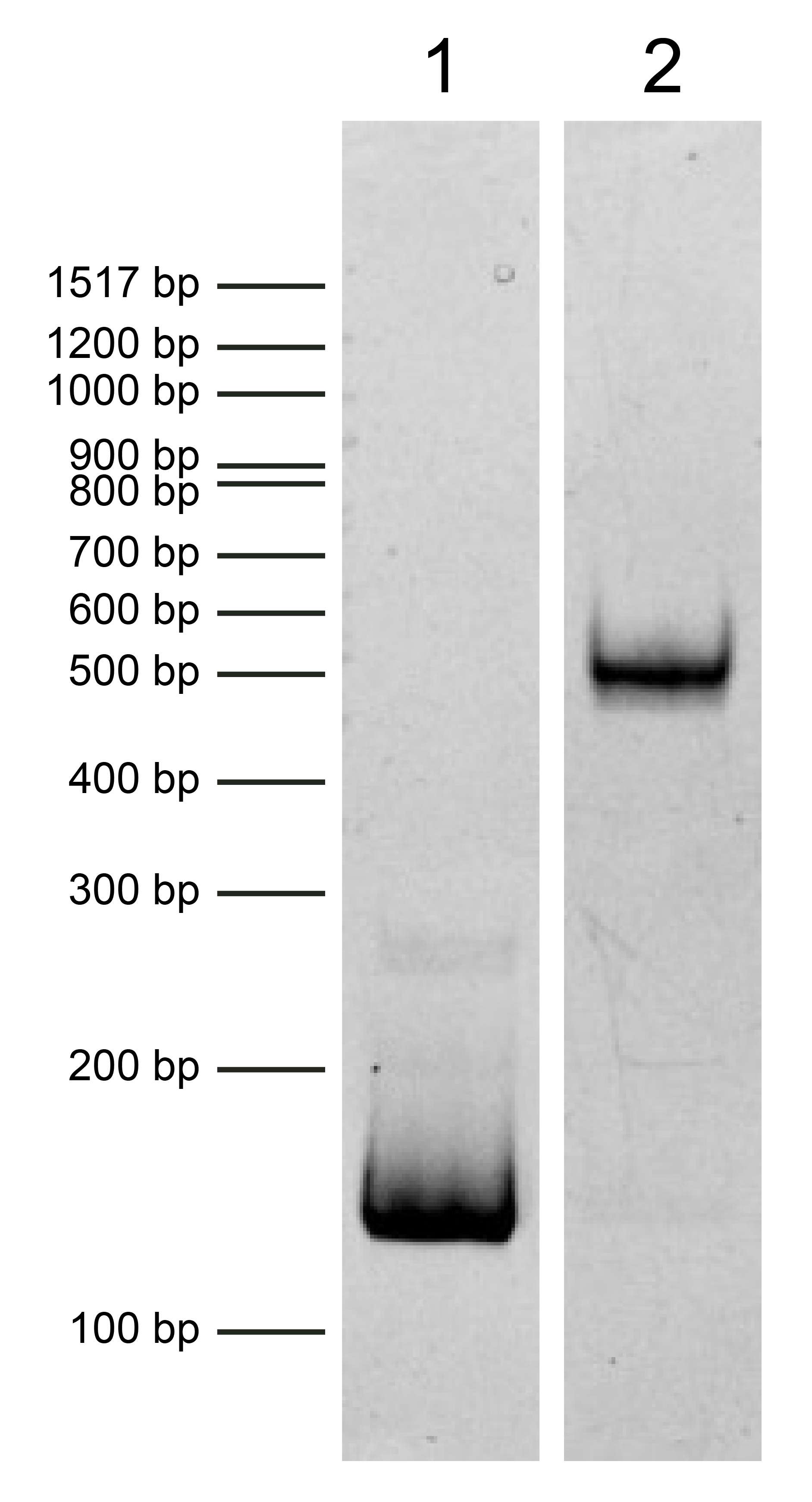
Figure 2: DNA gel data
Heterotypic [H3 • H3K4me3,K14ac] nucleosome resolved via native PAGE and stained with ethidium
bromide to visualize DNA. Both lanes are from the same gel. Lane 1: Free DNA (EpiCypher 18-0005; 75 ng). Free
DNA is over 95% pure by densitometry. Lane 2: Intact heterotypic [H3 • H3K4me3,K14ac]
nucleosomes (400 ng).
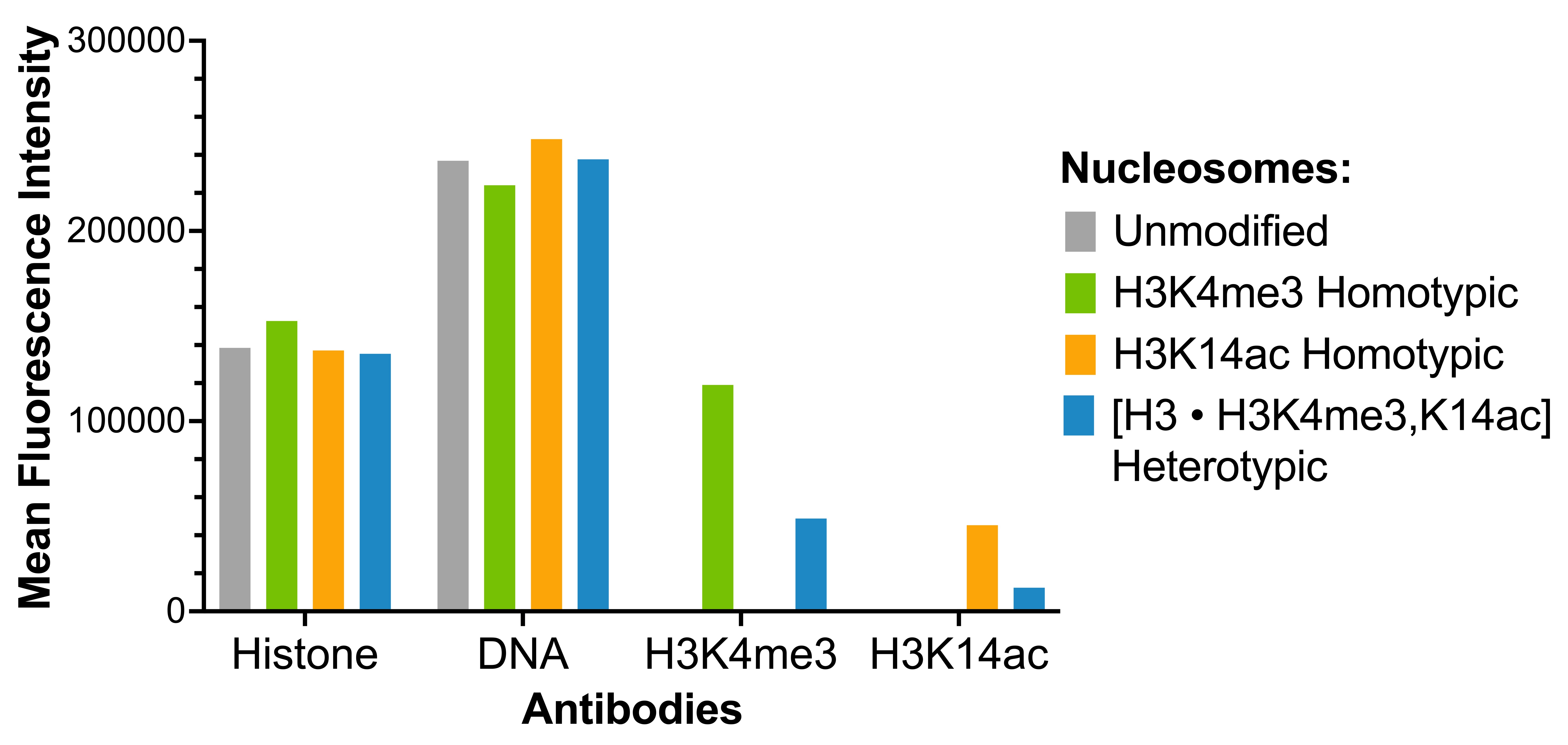
Figure 3: Luminex multiplexed specificity profiling
Heterotypic [H3 • H3K4me3,K14ac] nucleosome was assessed using a Luminex® based approach. The panel
comprises biotinylated designer nucleosomes individually coupled to color-coded Luminex MagPlex®
beads. Histone antibody (EMD Millipore MAB3422), DNA antibody (EMD Millipore MAB030), H3K4me3
antibody (EpiCypher 13-0060), and H3K14ac antibody (ThermoFisher MA5-32814) were added (x-axis),
and a second layer of anti-IgG*Phycoerythrin (PE; BioLegend 406421 for anti-rabbit IgG or BioLegend
405307 for anti-mouse IgG) was used for detection. Data were generated using a Luminex FlexMAP 3D®.
Histone and DNA antibodies bind nucleosomes in the panel equivalently, as expected. H3K4me3 antibody
and H3K14ac antibody bind heterotypic [H3 • H3K4me3,K14ac] nucleosomes at reduced strength in
comparison to homotypic H3K4me3 (EpiCypher 16-0316) and H3K14ac (EpiCypher
16-0343) nucleosomes.
Technical Information
Application Notes
Heterotypic [H3 • H3K4me3,K14ac] nucleosome is highly purified and suitable for a variety of applications, including use as a substrate in enzyme assays, high-throughput screening and inhibitor testing, chromatin binding studies, protein-protein interaction assays, structural studies, and in effector protein binding experiments. Trace amounts of TEV protease may be present (less than 5% of the preparation by densitometry, Figure 1). For a corresponding homotypic control, we recommend EpiCypher 16-0316 and/or EpiCypher 16-0343.
Gene & Protein Information
H2B - O60814 (alt. names: H2B K, HIRA-interacting protein 1)
H3.2 - Q71DI3
H4 - P62805
Documents & Resources
Related Products
![Heterotypic [H3K4me3 • H3K14ac] Recombinant Nucleosome, Biotinylated](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-y9o92/images/stencil/500x500/products/1167/1239/Heterotypic_Nuc_white__99511.1723235561.png?c=2)
![Heterotypic [H3K4me3 • H3K9,14,18ac] Recombinant Nucleosome, Biotinylated](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-y9o92/images/stencil/500x500/products/1168/1240/Heterotypic_Nuc_white__85489.1723235678.png?c=2)

![Heterotypic [H3 • H3K4me3] Recombinant Nucleosome, Biotinylated](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-y9o92/images/stencil/500x500/products/1164/1236/Heterotypic_Nuc_white__46729.1723235178.png?c=2)
![Heterotypic [H3 • H3K14ac] Recombinant Nucleosome, Biotinylated](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-y9o92/images/stencil/500x500/products/1165/1237/Heterotypic_Nuc_white__35995.1723235305.png?c=2)